The global tech community is leveraging various AI drawing tools to envision the future of smartphones. Concepts range from flexible designs to self-repairing screens, solar charging capabilities, and the use of advanced materials. Some of these ideas sound like something out of a science fiction movie. However, the realization of these technologies is imminent, and smartphones are set to undergo significant transformations in the coming years, surpassing our current imagination.
This article will discuss the future of smartphones and explore the trends in the development of mobile technology. Wendell Bell, a pioneer in the field of future studies, introduced a comprehensive model for considering the future. This framework includes three distinct categories: possible futures, probable futures, and desirable futures (Aligica 2011). This model can guide individuals and organizations in navigating the complexities of future-oriented thinking (Aligica 2011). This blog post will use these three categories to discuss the future of smartphones.
Possible future
By 2040, smartphones will no longer be limited to a fixed form. They might become smart wristbands worn on people’s wrists, using holographic projections to display information, allowing users to interact with touch controls in the air, watch videos, browse the web, and play games. Moreover, in 2040, smartphones will not just be devices for communication and entertainment. These smart wristbands will be equipped with multiple sensors to monitor users’ health in real-time, including heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and blood pressure, providing personalized health recommendations (as shown in Image 1)(Kumar et al. 2013). The devices will display health data through holographic projections, enabling users to stay informed about their health status at all times. This technology will not only enhance convenience but also promote intelligent health management. Additionally, smartphones will seamlessly connect with AR glasses, providing augmented reality experiences, such as displaying navigation information, real-time translation, and virtual assistants. In 2040, people won’t need to look at maps in real-time as they do today; smartphones will create routes to each destination and display them on the ground (as shown in Image 2). At that time, there will be no communication barriers, and people speaking different languages will be able to converse effortlessly by wearing these smart wristbands, eliminating concerns about language differences (as shown in Image 3).
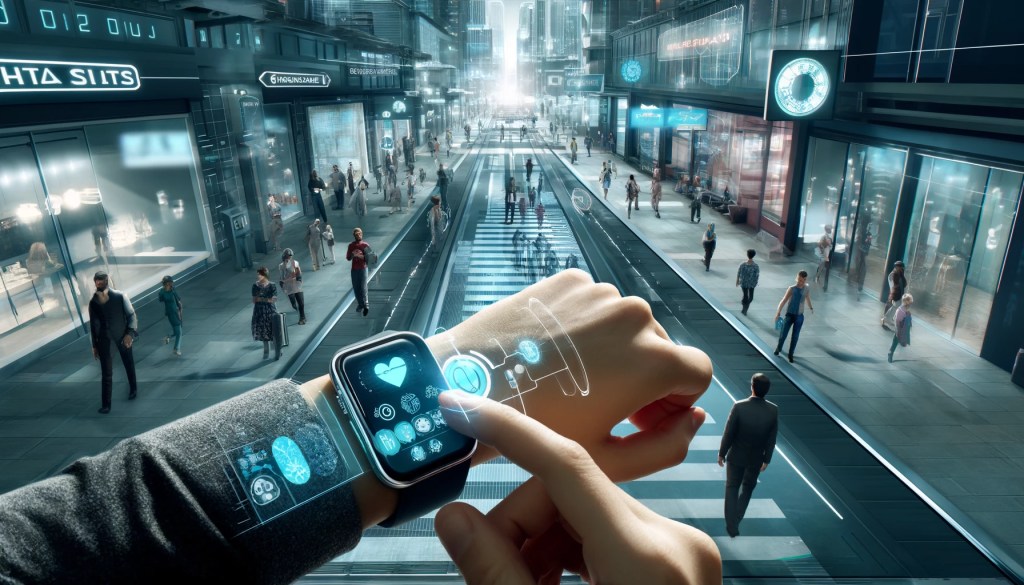

(Image 1)
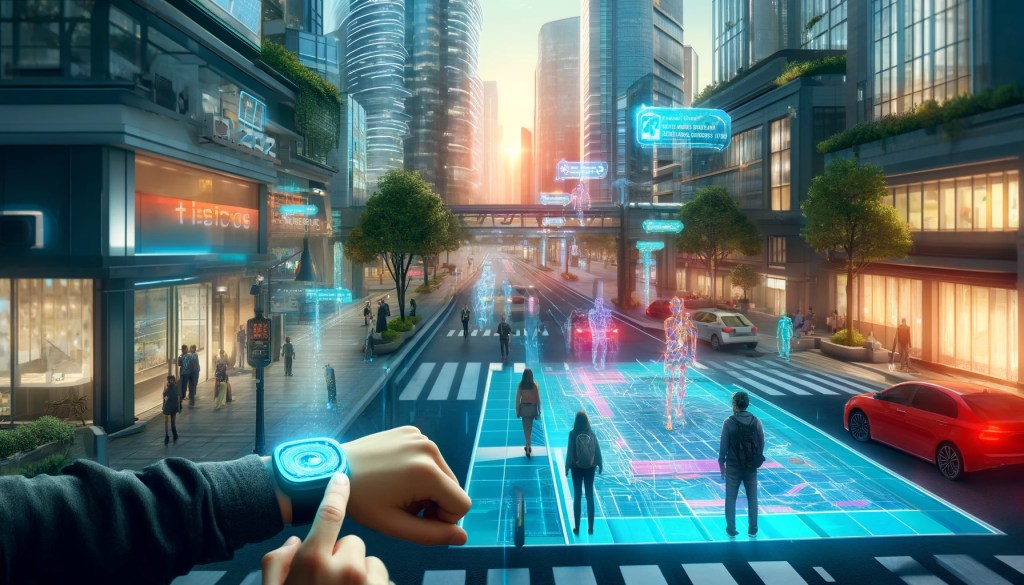

(Image 2)
(Image 3)
Probable future
By 2040, with continuous advancements in battery technology, future smart wristbands will have long-lasting battery life, supporting round-the-clock use. This means users will no longer need to charge frequently and can enjoy the convenience of smart wristbands for extended periods. Advanced battery technology will not only increase battery capacity and lifespan but also enable fast charging, allowing users to fully charge their devices in a short time. Smartphones will adopt solar charging technology, absorbing natural light to extend battery life further and reduce reliance on traditional charging methods (as shown in Image 1).
Moreover, in future smartphones, holographic projection technology will become more mature and widespread. Users will be able to view holographic displays of messages, notifications, and applications anytime, anywhere through their wristbands. This means that whether at home, in the office, or while traveling, users can see projected content in the air and interact with it using gestures (as shown in Image 2). For example, when receiving an important message or email, users only need to raise their wrist, and the holographic projection will display the relevant information in the air, allowing them to view and reply immediately. This technology not only improves the efficiency of information access but also provides a more intuitive and convenient user experience.
To achieve these advancements, smartphones in 2040 will be equipped with high-performance processors capable of handling complex tasks, including AI computations, real-time data analysis, and high-definition holographic displays. These processors will have powerful computing capabilities, allowing real-time analysis of users’ health data, environmental data, and more, providing intelligent suggestions and feedback (as shown in Image 3). Additionally, high-performance processors will support high-definition holographic displays, ensuring users enjoy a clearer and smoother visual experience.
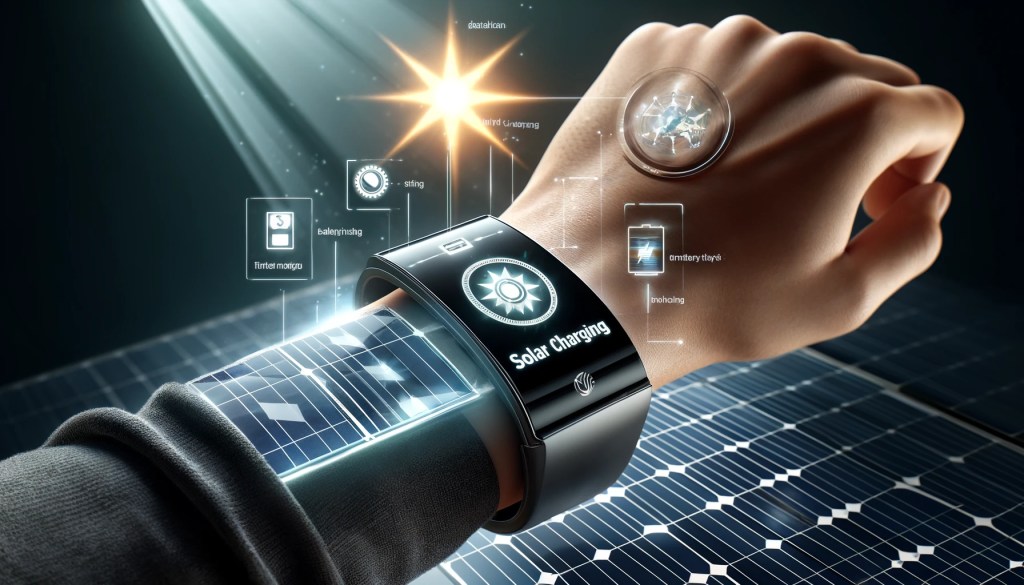

(Image 1)

(Image 2)

(Image 3)
Preferable future
By 2040, smartphones are expected to become powerful educational tools, providing personalized learning experiences and helping users acquire knowledge and skills anytime, anywhere. The smart wristbands will support online courses, virtual classrooms, and interactive learning applications. Students will be able to view course content, participate in discussions, and take exams via holographic projections(as shown in Image 1). Regardless of location, users can utilize their spare time to learn and enhance their skills. With the learning management system integrated into the smart wristbands, users can customize learning plans according to their interests and needs, receiving real-time feedback and guidance. This flexible and efficient educational approach will promote knowledge dissemination, personal growth, and reduce educational disparities.
Furthermore, by 2040, users will place greater emphasis on environmental protection. Consequently, smartphones will adopt eco-friendly materials and sustainable production processes to minimize environmental impact. For example, smartphone casings will be made from biodegradable plastics or recycled metals, and internal components will utilize low-power chips and energy-efficient display technologies (as shown in Image 2).. This approach will not only reduce electronic waste but also lower carbon emissions during production. Such eco-friendly design and sustainable practices will help protect Earth’s resources and set a precedent for other electronic product manufacturers to follow a more environmentally conscious path.

(Image 1)

(Image 2)
In an ideal future, smart wristbands and holographic projection technology will not only bring technological breakthroughs but also prioritize human-centered design, environmental protection, and social sustainability. This future will not only meet users’ needs but also enhance overall quality of life and social well-being, driving the world towards a greener, healthier, and more equitable future.
Reference:
Aligica, P, D 2011, “Wendell Bell: The futurist,” Futures : the journal of policy, planning and futures studies, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 563–564.
Checko, A, Christiansen, HL, Yan, Y, Scolari, L, Kardaras, G, Berger, MS & Dittmann, L 2015, ‘Cloud RAN for Mobile Networks-A Technology Overview’, IEEE Communications surveys and tutorials, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 405–426.
Moonis, Ali, Chung, Paul & Hinde, Chris (eds) 2003, Developments in Applied Artificial Intelligence 16th International Conference on Industrial and Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems, IEA/AIE 2003, Laughborough, UK, June 23-26, 2003, Proceedings 1st ed. 2003., Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Kumar, S, Nilsen, WJ, Abernethy, A, Atienza, A, Patrick, K, Pavel, M, Riley, WT, Shar, A, Spring, B, Spruijt-Metz, D, Hedeker, D, Honavar, V, Kravitz, R, Craig Lefebvre, R, Mohr, DC, Murphy, SA, Quinn, C, Shusterman, V & Swendeman, D 2013, ‘Mobile health technology evaluation: The mHealth evidence workshop’, American journal of preventive medicine, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 228–236.